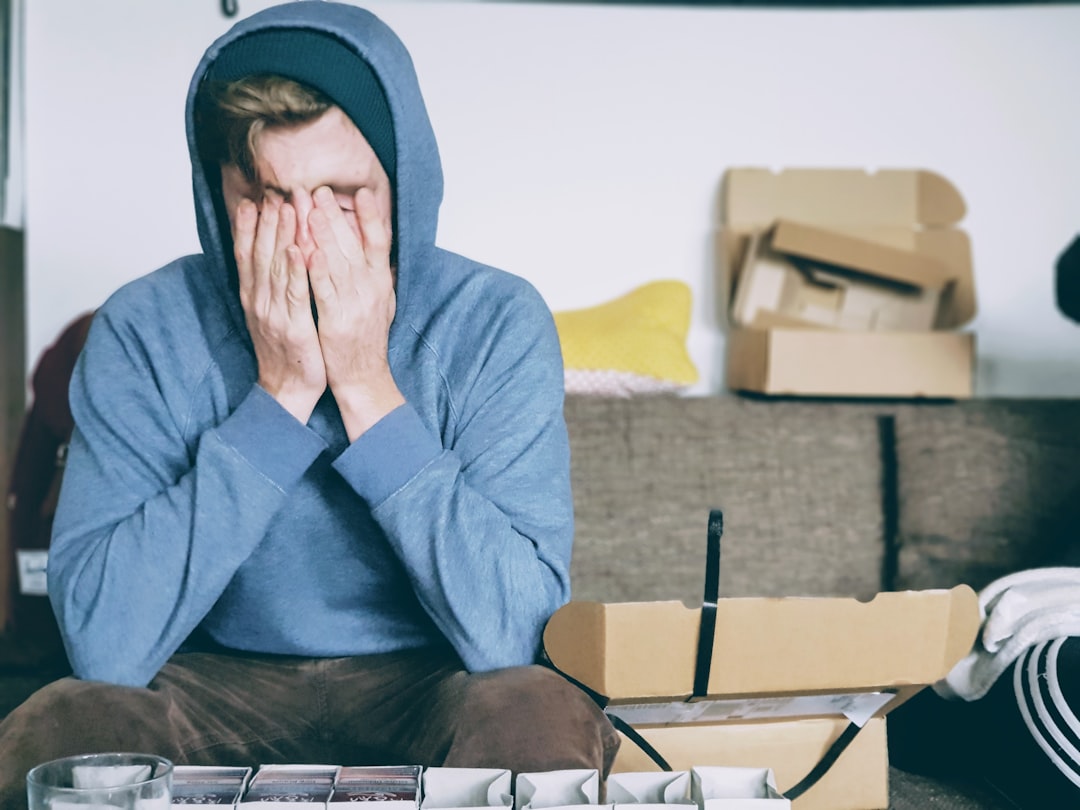
In the fast-paced world we live in, stress has become a ubiquitous companion in our daily lives. It’s the body’s natural response to challenges or demands, often described as a feeling of emotional or physical tension. While stress can sometimes serve as a motivator that helps us complete tasks or escape danger, chronic stress has a profoundly negative impact on our health. Understanding why stress is harmful is crucial to managing it effectively and maintaining overall well-being.
The Physiology of Stress
When you encounter a stressful situation, your body reacts by releasing hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. This is part of the “fight or flight” response, which prepares your body to act quickly. However, when stressors are always present and you constantly feel under attack, that fight-or-flight reaction stays turned on. The long-term activation of the stress-response system can disrupt almost all your body’s processes and increase the risk for numerous health problems.
Cardiovascular Health Risks
Chronic stress has been linked to heightened cardiovascular risks. Continuous stress can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, which over time can cause wear and tear on your heart and blood vessels. This heightened state of cardiovascular activity can lead to an increased risk of hypertension, stroke, and heart attacks.
Weakened Immune System
Stress stimulates the immune system, which can be advantageous for immediate situations. However, prolonged stress can weaken the immune response, leaving you more vulnerable to infections and illnesses. It can also slow down the healing process and contribute to the exacerbation of inflammatory conditions.
Mental Health Concerns
Perhaps one of the most well-known effects of stress is on mental health. Chronic stress is a significant trigger for mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. It can lead to feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, and can affect one’s self-esteem. Moreover, it can impair cognitive functions like concentration, memory, and decision-making.
Digestive System Disruption
Stress doesn’t only affect your brain; it also impacts your gut. It can alter your appetite (either increasing or decreasing it), lead to gastrointestinal issues such as indigestion, stomach cramps, constipation, or diarrhea, and exacerbate digestive conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Sleep Disturbances
High levels of stress often lead to sleep disturbances or insomnia due to the body’s inability to relax. Poor sleep quality can further compound the issue by impacting mood regulation, cognitive function, and even cardiovascular health.
Weight Gain
Cortisol plays a role in regulating metabolism. Under stress, cortisol levels can increase appetite and cravings for sugary or fatty foods. As a result, chronic stress can lead to weight gain or obesity, which in turn increases the risk for other health issues such as diabetes and heart disease.
Aging Acceleration
Chronic stress has been shown to affect cellular aging by shortening telomeres—the protective caps at the end of chromosomes—leading to accelerated aging processes within the body.
Behavioral Changes
To cope with stress, some individuals may resort to unhealthy behaviors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, overeating, or drug use. These coping mechanisms may temporarily relieve stress but ultimately lead to additional health problems.
Managing Stress for Better Health
Recognizing the adverse effects of chronic stress underscores the importance of developing effective stress management strategies. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, regular exercise, adequate sleep, healthy eating habits, seeking social support, and professional help when needed are essential in mitigating the harmful impacts of stress on your health.
In conclusion, while it is impossible to eliminate all sources of stress from our lives completely, understanding its potential harm is a critical step towards managing it effectively. By adopting healthier coping mechanisms and lifestyle choices, we can reduce our stress levels and protect our health from its detrimental effects.